Understanding Moving Averages: SMA, EMA, and WMA for Smarter Forex Trading
If you’re starting in Forex trading, one of the most common tools you’ll encounter is the moving average. Whether you’re analyzing the EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, or USD/CAD, moving averages help traders identify trends, spot potential reversals, and make more informed decisions. But with different types like SMA, EMA, and WMA, understanding how each works is crucial.
 https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
What Are Moving Averages?
A moving average is a technical analysis tool that smooths out price data over a set period, helping traders see the overall direction of a currency pair rather than getting lost in daily fluctuations. Think of it like watching a car’s speedometer averaged over several minutes—it gives a clearer picture than just looking at each second.
In Forex, moving averages are commonly applied to closing prices of currency pairs to track trends over time. They are not perfect predictors, but they provide a solid foundation for making trading decisions, especially for beginners.
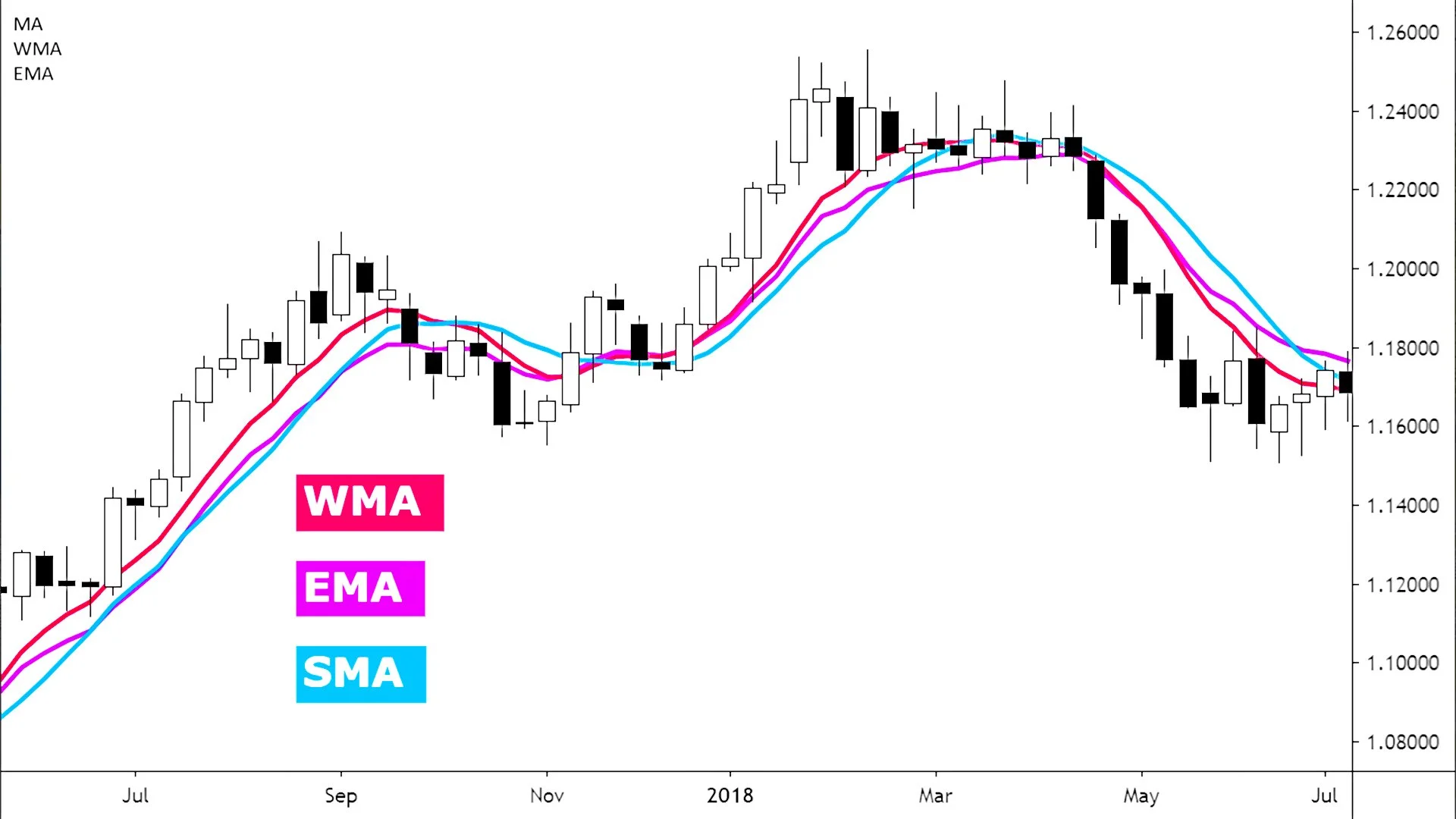
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is the most basic type. It calculates the average of a set number of past prices. For example, a 10-day SMA of EUR/USD takes the closing prices of the last 10 days, sums them up, and divides by 10.
Pros of SMA:
Easy to calculate and understand
Smooths out minor price fluctuations
Works well for identifying long-term trends
Cons of SMA:
Reacts slowly to sudden price changes
May lag behind the market during rapid trend shifts
In Forex trading, SMA is often used to identify support and resistance levels or confirm whether a currency pair is trending up or down.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to market changes. For instance, a 10-day EMA reacts faster to price moves in USD/JPY than a 10-day SMA because it emphasizes the latest data.
Pros of EMA:
Reacts quickly to price changes
Useful for spotting short-term trends and reversals
Preferred for fast-moving Forex markets
Cons of EMA:
More sensitive to market noise, which can lead to false signals
EMAs are widely used by Forex traders to catch early signals of trend changes or to time entry and exit points in volatile markets.
Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
The Weighted Moving Average (WMA) is similar to EMA but assigns a specific weight to each price in the period. The most recent price gets the highest weight, while older prices gradually decrease in importance.
Pros of WMA:
More precise than SMA and EMA for trend detection
Reduces lag while still smoothing data
Helpful for short-term Forex trading strategies
Cons of WMA:
Slightly more complex to calculate
Can be overly sensitive in choppy markets
WMAs are particularly useful for traders who want a balance between speed and reliability when analyzing currency pairs like GBP/USD or AUD/USD.
Why Moving Averages Matter for Forex Trading
Trend Identification: Moving averages show whether a currency is in an uptrend, a downtrend, or a sideways market.
Support & Resistance: They often act as dynamic levels where prices bounce or reverse.
Crossovers: When a short-term moving average crosses a long-term one, it can signal potential buying or selling opportunities. For example, when a 50-day EMA crosses above a 200-day EMA, it may indicate a bullish trend.
Risk Management: Helps traders avoid chasing the market and make decisions based on objective data.
Practical Example
Imagine you’re analyzing EUR/USD:
The 50-day SMA shows a steady upward slope → long-term trend is bullish.
The 10-day EMA starts crossing above the 50-day SMA → short-term momentum is picking up.
WMA confirms the strength of the recent price surge → traders may consider entering a buy position.
This combination helps Forex beginners and seasoned traders alike make decisions with more confidence.
Key Takeaways
SMA is simple and reliable for long-term trends.
EMA reacts faster and is ideal for short-term trends and volatile markets.
WMA balances responsiveness and accuracy, perfect for traders looking for precision.
Understanding these moving averages can improve your Forex trading strategies and reduce emotional decisions.
Start trading smarter today! Join GME Academy’s FREE Forex workshop to learn how to apply SMA, EMA, and WMA in real-time Forex trading and spot profitable opportunities across USD, EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, and other major currency pairs.

