Speed vs. Stability: Mastering Adaptive Moving Averages (KAMA and HMA)
In the volatile world of Forex trading, traditional moving averages like the Simple Moving Average (SMA) often suffer from a classic dilemma: they are either too slow (lagging) or too sensitive (generating false signals). To bridge this gap, professional traders and students at Global Markets Eruditio turn to Adaptive Moving Averages.
Unlike static indicators, adaptive averages like Kaufman’s Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA) and the Hull Moving Average (HMA) dynamically adjust their internal logic based on market conditions. Understanding these tools is essential for anyone looking to master Forex trading for beginners and beyond.
 https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
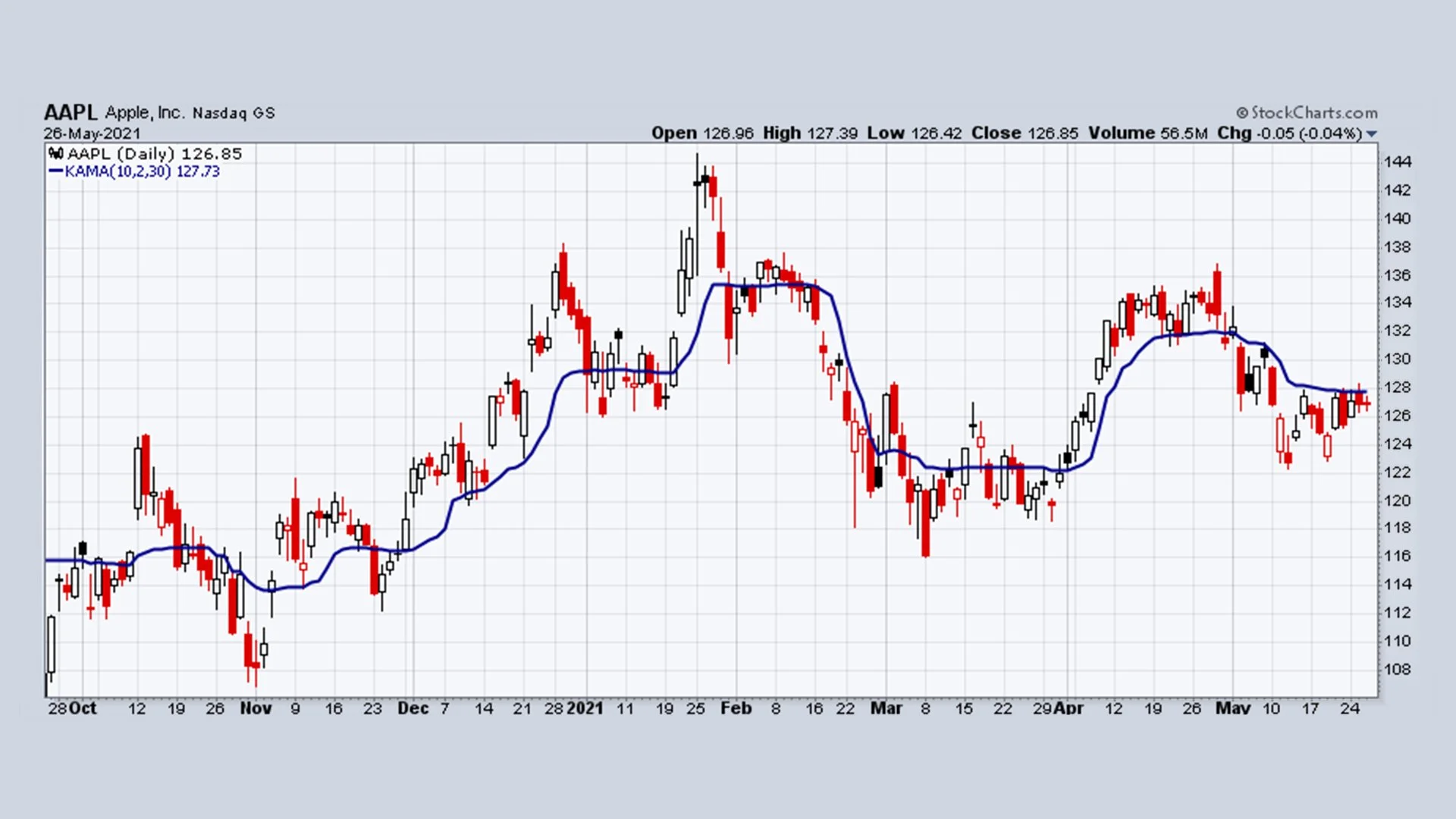
Kaufman’s Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA): The Volatility Filter
Developed by Perry Kaufman, KAMA is designed to navigate "noisy" markets. Its genius lies in its ability to speed up when the market is trending clearly and slow down when the price is moving sideways.
How KAMA Works: The Efficiency Ratio (ER)
The heart of KAMA is the Efficiency Ratio (ER).
Trending Markets: When the price moves steadily in one direction, the ER approaches 1. KAMA becomes highly sensitive, tracking the price closely like a fast EMA.
Choppy Markets: When the price is bouncing around without direction, the ER drops toward 0. KAMA "flattens out," ignoring the minor price spikes (noise) to prevent you from being "whipsawed" out of a trade.
Hull Moving Average (HMA): The Speed Demon
If KAMA is about filtering noise, the Hull Moving Average (HMA) is about eliminating lag. Created by Alan Hull, the HMA uses a unique mathematical approach involving weighted moving averages and square roots to create a curve that is incredibly responsive.
The HMA Advantage:
Zero-Lag Feel: The HMA stays closer to the current price than almost any other moving average. This makes it a favorite for scalpers and day traders.
Extreme Smoothness: Despite its speed, the HMA avoids the "jagged" look of other fast indicators, providing a clear visual of the trend's slope.
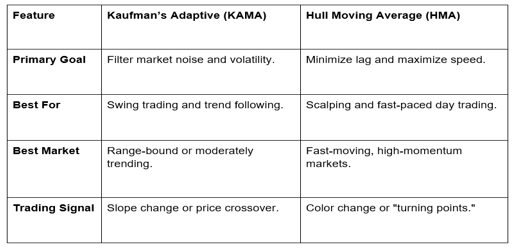
KAMA vs. HMA: Which One Should You Use?
 https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
Practical Application: Trading the US Dollar and Major Pairs
At GME Academy, we teach that moving averages are not just lines on a chart—they are proxies for institutional value.
Trend Confirmation: Use a long-period HMA (e.g., 50 or 100) to determine the "anchor trend" of the US Dollar (USD). Only take trades in the direction of the HMA's slope.
Entry Timing: Use KAMA as a dynamic support/resistance level. In a bullish EUR/USD trend, wait for the price to pull back to the KAMA line. If the line remains flat or starts to curve up, it’s a high-probability entry point.
Confluence: Never trade an adaptive average in isolation. Combine them with RSI for momentum or BOS/CHOCH for structural confirmation.
Elevate Your Technical Edge
Moving averages are the bread and butter of technical analysis, but adaptive versions give you the professional edge needed in 2026's fast-moving markets. By selecting the right average—speed with the HMA or stability with KAMA—you align your strategy with the current "character" of the market.
Join our FREE Forex Workshop today and let the experts at Global Markets Eruditio show you how to set up these advanced indicators on your platform. We’ll help you fine-tune your settings for the Canadian Dollar (CAD), GBP/JPY, and more, so you can trade with institutional-grade precision.

