Master the Market Math: Calculating Risk-Reward Ratio Like a Pro
In the world of Forex Trading, successful long-term outcomes aren't solely determined by how often you win, but rather by how much you win when you are right versus how much you lose when you are wrong. This crucial balance is quantified by the Risk-Reward Ratio (R-R Ratio), a fundamental concept that separates informed traders from mere gamblers.
Understanding and calculating the R-R Ratio is the cornerstone of effective risk management and trade sizing. It is the core mathematical discipline taught at the GME Academy that enables traders to protect capital and maximize profitable opportunities in volatile markets, whether trading major currency pairs like EUR/USD or crosses like GBP/JPY.
 https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
What is the Risk-Reward Ratio?
The Risk-Reward Ratio is the quotient of your potential loss on a trade (the risk) divided by your potential gain on that same trade (the reward).
In simple terms: R-R Ratio = Potential Loss / Potential Gain
Before initiating any trade—whether you're practicing Forex Trading for Beginners or executing an advanced strategy—you must first determine two essential price levels:
Stop-Loss (SL): The price level at which you will exit the trade to limit your loss. This defines your Risk.
Take-Profit (TP): The price level at which you will exit the trade to secure your profit. This defines your Reward.
The distance between your Entry Price and your Stop-Loss level (measured in pips) is your Risk, and the distance between your Entry Price and your Take-Profit level (measured in pips) is your Reward.
The Pro's Guide to Calculation
To calculate the R-R Ratio, you simply need to follow these three steps:
Step 1: Determine the Risk (The Denominator)
The risk is the distance (in pips) between your intended Entry Price and your Stop-Loss (SL) level.
● Example Trade (Long EUR/USD):
Entry Price: 1.0850
Stop-Loss (SL): 1.0820
Risk Calculation: $1.0850 - 1.0820 = 0.0030$
Risk in Pips: 30 pips.
Step 2: Determine the Reward (The Numerator)
The reward is the distance (in pips) between your intended Entry Price and your Take-Profit (TP) level.
● Example Trade (Long EUR/USD):
Entry Price: 1.0850
Take-Profit (TP): 1.0940
Reward Calculation: $1.0940 - 1.0850 = 0.0090$
Reward in Pips: 90 pips.
Step 3: Calculate and Interpret the Ratio
The final step is to divide the Risk by the Reward, and then express the ratio in the format Risk: Reward (1: X).
Calculation: Risk (30 pips): Reward (90 pips)
Divide both sides by the Risk (30 pips): $30/30: 90/30$
R-R Ratio: 1:3
A 1:3 Risk-Reward Ratio means you are risking 1 pip to gain 3 pips. In other words, your potential profit is three times greater than your potential loss.10 This is the hallmark of trading like a pro
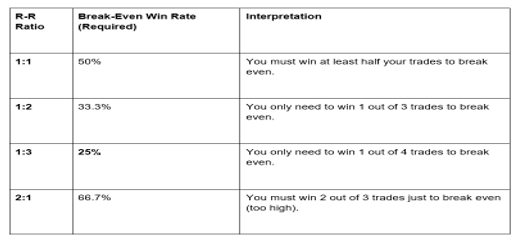
The Win-Rate Connection: Why R-R Ratio is King
A common misconception in Forex is that a high win rate guarantees profitability. This is false. A trader with a low win rate can still be profitable if their R-R Ratio is high, and vice versa.
The R-R Ratio determines the minimum win rate you need to simply break even, known as the Break-Even Win Rate.
 https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
Professional traders often target a minimum R-R Ratio of 1:2 or 1:3. Why? Because it grants a massive psychological and capital cushion: you can afford to be wrong more often than you are right, and still make money.
💡 Pro Insight: Aiming for a ratio of 1:3 means even if you only win 30% of your trades, you will be profitable, assuming a consistent trade size.
Practical Application: Integrating R-R into Your Strateg
Calculating the R-R Ratio is not a one-time thing; it's an integral part of the trade setup, essential for disciplined trading in any market, including the US Dollar (USD) pairs.
Establish Targets First: Use technical analysis (support/resistance, Fibonacci levels) to determine your logical Take-Profit (Reward) and Stop-Loss (Risk) levels before calculating the R-R Ratio.
Reject Low-Ratio Trades: If your analysis yields a ratio worse than 1:1.5 (e.g., 2:1 or 1:1), simply do not take the trade. There will always be a better setup. Trading like a professional means being patient and waiting for favorable mathematical odds.
Position Sizing: Once the R-R Ratio is acceptable, use the Risk in Pips (Step 1) to accurately calculate your trade size (lot size) such that your total monetary loss, should the Stop-Loss be hit, is only 1-2% of your total account equity.
Mastering this core piece of market math is not about finding the perfect trade; it's about perfecting your approach to capital preservation and opportunity evaluation.
Stop Guessing. Start Calculating.
The Risk-Reward Ratio is the most potent weapon in a successful trader’s arsenal. It forces discipline, clarifies potential outcomes, and ensures that you are mathematically positioned for long-term profitability. If you are struggling with inconsistent results in the volatile Forex market, the answer lies not in finding better signals but in perfecting your risk management structure.
Ready to incorporate this professional-grade discipline into your strategy and trade with mathematical confidence?
Join our FREE Forex Workshop today! We provide essential lessons on Forex Trading for Beginners, focusing heavily on mastering risk management and position sizing, the true keys to trading success.
Click here to reserve your spot and start calculating your success like a pro!

