The Business of Pips: How Forex Brokers Make Money
In the fast-paced world of Forex trading, brokers are often seen simply as the "gatekeepers" to the global markets. However, a broker is not just a facilitator; it is a business with sophisticated revenue models designed to profit regardless of whether the market goes up or down.
For the GME Academy, understanding "Broker Economics" is the first step toward becoming a professional trader. If you don't know how your broker makes money, you don't know where your own risks truly lie.
 https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
1. The Primary Engine: The Bid-Ask Spread
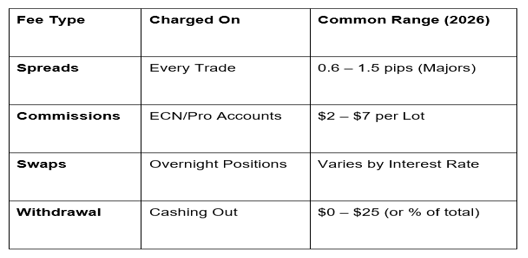
The most common way a broker earns is through the spread—the difference between the "Buy" (Ask) price and the "Sell" (Bid) price.
The Markup: Think of a broker like a money changer at the airport. They buy a currency at a lower price and sell it to you at a higher price. This "gap" is their immediate profit on every single trade you execute.
Variable vs. Fixed: In 2026, most top-tier brokers offer variable spreads. During high-impact news (like the recent NZD unemployment data), these spreads can "widen" significantly, increasing the broker's profit margin while making it harder for traders to hit their targets.
2. Account Execution Models: A-Book vs. B-Book
Behind the scenes, brokers use two main business models to handle your trades. This is where the real "broker secrets" are kept.
A-Book (The Agency Model)
The broker acts as a middleman. They send your trade directly to Liquidity Providers (big banks like JP Morgan or Citibank).
How they profit: They charge a commission per trade or add a small "markup" to the raw spread they get from the bank.
Conflict of Interest: None. They want you to win because successful traders trade more frequently and for longer periods.
B-Book (The Market Maker Model)
The broker "takes the other side" of your trade. They don't send your order to the market; they fill it internally.
How they profit: If you lose, the broker wins. Your loss becomes their direct revenue.
The Reality: Most retail brokers in 2026 use a Hybrid Model. They A-Book their profitable "pro" traders and B-Book the beginners who statistically lose their capital within 90 days.
3. The "Hidden" Costs: Swaps and Financing
Forex is a leveraged product, meaning you are essentially "borrowing" money from the broker to control larger positions. This loan isn't free.
Swap Fees (Rollovers): If you hold a position past 5:00 PM EST, the broker applies a "Swap" fee based on the interest rate difference between the two currencies. While you can sometimes earn a positive swap, brokers often bake a small "financing spread" into the rate, ensuring they take a cut of the interest.
Inactivity Fees: Many platforms now charge a monthly fee (typically $10–$20) if you haven't logged in or traded for 6 to 12 months.
4. Leverage and Volume: The Profit Multiplier
Brokers offer high leverage (e.g., 1:100 or 1:500) to encourage larger "Lot Sizes."
Volume-Based Revenue: Since most broker fees are calculated based on the size of the trade, a trader using high leverage is generating significantly more "spread revenue" for the broker than a trader using 1:1 leverage.
 https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/619b666b5842697e2af69258/a9d57b27-4fad-4532-874a-89133d6a85bc/P477.02.jpg?content-type=image%2Fjpeg
The GME Academy Analysis: "Choose the Model, Not the Bonus"
At Global Markets Eruditio, we always tell our students: "If the spread is free, YOU are the product." Brokers offering "Zero Spreads" and "No Commissions" are almost certainly B-Booking your trades and profiting from your losses.
How to Protect Your Capital:
Demand Transparency: Ask your broker if they are a "No Dealing Desk" (NDD) or a Market Maker.
Calculate the Round-Trip: Always factor in both the spread and the commission before entering a trade.
Check for Slippage: If you consistently get filled at a worse price than you clicked, your broker might be "harvesting" extra pips from your execution.
Join our FREE "Broker Secrets" Webinar
Learn how to read a Broker's Terms & Conditions to find hidden fees. We’ll show you how to test for "B-Book manipulation" and which 2026 brokers offer the most transparent A-Book execution for serious traders.

